Class 12 Economics Solved Question Paper 2024
Solved past year question papers are very helpful resource material for students to get maximum marks in final exams of CBSE. These papers help student to know the pattern of questions asked in final CBSE exams. Economics, a tough subject at senior secondary level, requires a thorough preparation to get good marks.
Table of Content
ToggleIn view of this, here we are providing you CBSE class 12 Economics solved question paper of 2024. The code no. of the solved paper is 58/2/1 as conducted by CBSE in 2024 final exams.
In this article, we are providing solutions to MCQs with explanation. Moreover, model answer for subjective questions have also been provided in very easy language.
Section A - Introductory Macro Economics
Q.1 Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: A consumption function describes the relationship between consumption and savings.
Statement 2: Consumption function consists of two components – autonomous consumption and induced consumption.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
(A) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(B) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(C) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
(D) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false
Answer: (B) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
Explanation: A consumption function describes functional relationship between income and consumption. It does not show relationship between consumption and saving. Consumption function can be written as below:
C = C̅ + bY
In the above equation consumption has two components. One is Autonomous Consumption denoted by C̅ while bY denotes Induced Consumption. Autonomous Consumption does not depend on level of Income while Induced Consumption increases with increase in income and decreases with decrease in Income.
Q.2 Identify which of the following is not one of the merits of fixed exchange rate system.
(A) Ensures stability in exchange rate
(B) Possibility of under or over valuation of foreign currency
(C) Prevents speculations in foreign exchange market
(D) Coordination of macroeconomic policies becomes convenient.
Answer: Possibility of under or over valuation of foreign currency
Explanation: In the Fixed Exchange Rate System, the government decides the exchange rate of domestic currency against the foreign currency. The government may fix the exchange rate of its currency below or above the market exchange rate. As such, there is possibility of under or over valuation of foreign currency.
Example – Suppose Indian Government has fixed exchange rate between Rupee and US Dollar as INR20 : USD1. However, if real market value of USD 1 is INR 15, then US Dollar is overvalued. In contrast, if the government fixes exchange rate as INR10 : USD1, then the US Dollar is undervalued as it could now fetch only INR 10 for 1 dollar against its real market value of INR 15.
Q.3 Identify which of the following will appear on the debit side in the Capital Account of India’s Balance of Payments.
(A) An Indian sending remittances from England.
(B) Investing in assets abroad by Indians.
(C) An American company purchasing shares of an Indian company.
(D) Export of spices from India.
Answer: (B) Investing in assets abroad by Indians.
Explanation: In Balance of Payment Account (BoP), the monetary transactions going out of the country are recorded on the Debit Side while those coming into the country on Credit Side. Further, in Capital Account of BoP, only those transactions are included which affect liabilities and assets of a country.
In the above question, option B and C are related to Capital Account. Option A and D are related to Current Account of BoP as they do not affect assets or liabilities of India.
In Option B, action of Investing in assets abroad by Indians causes outflow of money from India, resulting in increase of India’s assets. As such, this transaction will be recorded on the Debit Side of Capital Account in BoP.
In Option C, action of an American company purchasing shares of an Indian company causes inflow of foreign exchange and also decreases assets of India. So, it will be recorded on Credit Side of Capital Account.
Q.4 Study the following figure carefully and choose the correct alternative to fill in the blank.
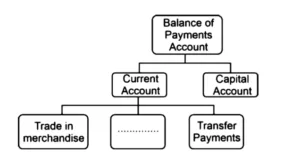
Credit: CBSE
Alternatives:
(A) Investments
(B) Trade of Services
(C) External Borrowings
(D) External Assistance
Answer: (B) Trade of Services
Explanation: Current Account is one the two parts of Balance of Payments Account. Monetary Transaction related to following three components are included in Current Account:
Trade in Merchandise (Trade in Goods) – It is trade of physical or tangible (which can be seen or touched) items. It is also called trade of visible items as we can see traded items crossing the boundary of two countries. Example – Export of Coal from India to Thailand.
Trade of Services – It is trade of intangible (which cannot be seen or touched) items. It is also called trade of invisible items as we cannot see the traded items crossing the boundary of two nations. Example – A teacher teaching online to foreign students and getting payment in foreign currency.
Transfer Payments – These are unilateral (one sided) transactions for which no service or commodity is expected in return. They are free in nature. They do no create any liability on the receiver. They are also part of invisible items in Current Account of BoP. For the current year of accounting, they are called Current Transfers.
Q.5 Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: Economic territory and political frontier of a nation are one and the same thing.
Statement 2: American Embassy in India is a part of the economic territory of India.
(A) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(B) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(C) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
(D) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer: (D) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
Explanation: Political frontier separates one country from another country physically. Like, we have political borders with countries like Pakistan, China, Bangladesh. The territory within political frontiers of a country is under legal control of a that particular country. This is the sovereign land of a particular country where all the political activities like elections, social and economic activities are conducted.
In contrast to this, Economic Territory is a geographical area where person, capital and goods of a country frequently circulate. For example, Indian Ships, Airplanes operating in other country’s boundary come under Economic Territory of India. Economic Territory can be broader than the political territory of a country.
American Embassy in India is not a part of the economic territory of as persons, capital and goods of India cannot freely circulate in it. In contrast. Indian Embassy in America is part of India’s Economic Territory where Indian persons, capital and goods can freely circulate.
Q.6 Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: Money is a commodity which is generally accepted as a medium of exchange.
Statement 2: Money solved the problem of double coincidence of wants.
(A) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(B) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(C) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
(D) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer: (C) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
Explanation: Primary function of Money is to act as medium of exchange for goods & services. In barter system, there was problem of Double Coincidence of Wants. It means that exchange of goods between two persons could happen only when one person would possess the good which the other person needed.
For example, there are two persons. One needs shoes while other needs a pot. The exchange could happen between them only if they need each other’s good. If the person who has shoes but need pot does not want to sell shoes to the other person who needs shoes but has the pot, then exchange of goods cannot happen.
But the money solved this problem as one person can now buy desired goods with money. The receiver of money can buy his desired goods from others with the received money.
Q.7 Suppose in an imaginary economy, autonomous consumption = Rs 500 crore and marginal propensity to consume = 0.8. The saving function for the economy would be _________.
(A) 500 + 0.8Y
(B) (-) 500 + 0.8Y
(C) 500 + 0.2Y
(D) (-) 500 + 0.2Y
Answer: (D) (-) 500 + 0.2Y
Explanation: The consumption function can be written as
C = C̅ + bY
Where C̅ is autonomous consumption and b is Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC).
We can derive Saving function from consumption function as below:
S = – C̅ + (1-b)(Y)
S = – C̅ + MPS (Y) (MPS + MPC = 1 or MPS = 1 – MPC) (MPS=Marginal Propensity to Save.
So with the given data, we can write Saving Function as
S = – 500 + (1-0.8)(Y)
S = – 500 + 0.2 (Y)
Q.8 Read the following statements: Assertion (A) ad Reason (R). Choose the correct alternative from those given below:
Assertion (A): The maximum value of Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) can be unity.
Reason (R): At the break-even level of Income, savings are zero.
Alternatives:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
Answer: (B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation: We know that MPC + MPS = 1. As such, MPS can be unity or equal to 1 only then when MPC is zero (0). It means, MPS to be 1, consumer will have to save all his additional income and do no expenditure from the additional income.
Break Even Point is that point where Income and Consumption are equal to each other. Hence, saving is zero at this point.
Though B is true, it is not the Reason for MPC being zero.
Q.9 Identify the incorrect statement with reference to Cash Reserve Ration (CRR):
(A) It is a certain percentage of demand and time deposit liabilities that every bank must keep as cash reserves with the central bank.
(B) It is fixed by the Central Bank.
(C) It is not binding on the commercial banks.
(D) It is a tool used by the Central Bank to Control the credit creation in the economy.
Answer: (C) It is not binding on the commercial banks.
Answer: Cash Reserve Ratio is an important quantitative instrument of Central Bank through which it can control credit creation in the economy. It is fixed by the Central Bank as a percentage of demand and time liabilities of bank. Every bank has to maintain the cash reserve ratio mandatorily and keep it in cash with the Central Bank.
Q.10 Read the following statements: Assertion (A) ad Reason (R). Choose the correct alternative from those given below:
Assertion (A): The equilibrium level of income is determined, when ex-ante spending and ex-ante output are equal.
Reason (R): The equilibrium level of income may or may not be the same as the full employment level of output.
Alternative:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
Answer: Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: State of equilibrium is achieved when Aggregate Demand (Ex-ante Spending) is equal to Aggregate Supply (Ex-ante Output). At the level of AD = AS, equilibrium Income/GDP is also determined.
As per Economist JM Keynes, equilibrium can be obtained both at full employment level and below full employment level. So, in the state of equilibrium, level of income may or may not be the same as the full employment level of output.
11.(a) Accommodating transactions are undertaken to maintain stability in Balance of Payment. Justify the given statement with valid explanation.
Answer: It is true that Accommodating Transactions are undertaken to maintain stability in Balance of Payment. Apart from Accommodating Transactions, there are Autonomous Transactions in Balance of Payment. These are main transactions in BoP and are done with a motive of making profit. They are the reason that there is an imbalance (Surplus or Deficit) in Balance of Payment.
To correct this imbalance, accommodating transactions are made in the Balance of Payment Account. These are transactions are free from motive of profit. They are mainly undertaken by the government/central bank through movement in its Official Reserve Account.
OR
(b) “Depreciation of currency may promote exports of a nation” Defend or refute the given statement with valid arguments.
Answer: The statement is defended. There are following arguments in support of this statement:
- When domestic currency depreciates, its value decreases compared to foreign currencies. This makes domestic goods & services cheaper in international market.
- As a result, foreigners would demand more for domestic goods and services. In this way exports will increase.
In this way, we can see that depreciation of currency may increase exports for a country.
Q.12.On the basis of the data given below, estimate the value of Gross National Product at Factor Cost (GNPFC):
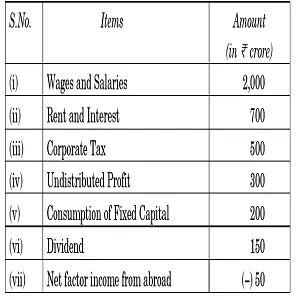
Credit: CBSE
Answer: We can use Income Method for Calculating GNP at Factor Cost from data.
As per the given data:
NDP at FC = Wages and Salaries + Rent and Interest + Corporate Tax + Undistributed Profit + Dividend
NDP at FC = 2000 + 700 + 500 + 300 + 150 = 3650
Now
NNP at FC = NDP at FC + Net Factor Income From Abroad
= 3650 + (-50)
= 3600
At last:
GNP at FC = NNP at FC + Depreciation (Consumption of Fixed Capital)
= 3600 + 200
= 3800
Q.13. For a hypothetical economy, assume the government increased an infrastructural investment by ₹10,000 crore. 80% of additional income is consumed in the economy. Estimate the increase in income and the corresponding increase in consumption expenditure in the economy. 4
Answer: Increase in investment stimulates increase in income manifold. However, it depends on value of Investment Multiplier. Value of Investment Multiplier depends upon the value of Marginal Propensity to Consume.
Based on the information in the question:
Increase in Investment = ₹10,000
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) = 80% or 0.8
Investment Multiplier (K) = 1/1-MPC
= 1/1-0.8 = 1/0.2 = 5
Increase in Income = Increase in Investment x K
= 10000 x 5 = 50000
Increase in Consumption = 80% or 0.8 of Increase in Income
= 0.8 x 50000 = 40000
14.(a) If actual demand for final goods falls short of the actual output of final goods corresponding to full employment level, it may lead to an unintended accumulation of inventories. Do you agree with the given statement? Give valid reasons in support of your answer. 4
Answer: Yes, I agree with the given statement. We can understand it with the following process:
- At full employment level when actual aggregate demand for goods falls short of actual aggregates supply/output, it would imply that there is more production/supply of goods in the economy than the demand of goods.
- In this case, producers will be left with unsold stock of goods. This unsold stock will lead to increase in undesired or intended inventories.
- In this situation, they will be bear loss equivalent to accumulation of unintended inventories.
So, we can say that unintended accumulation of inventories is the result of actual Aggregate Output of goods being more that the actual Aggregate demand of goods.
OR
(b) Complete the following table. Construct the consumption function at ₹200 crore level of income. 4
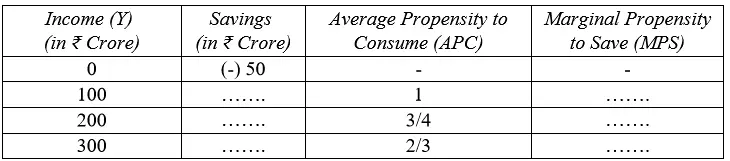
Credit: CBSE
Answer:
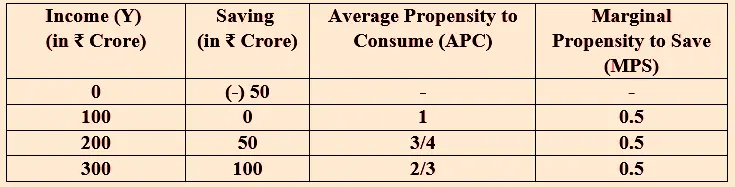
Consumption Function = C̅ + bY
= 50 + 0.5Y
= 50 + 0.5 (200)
= 50 + 100
= 150
How we solved this (Not to be included in answer)
We know that:
C = C̅ + b Y (C̅ = autonomous consumption/consumption at 0 level of income)
(b = Marginal Propensity to Consume)
S = – C̅ + (1-b) Y
= – C̅ + MPS (Y) (-C̅ = Autonomous Saving/Saving at 0 level of income)
(1-b/MPS = Marginal Propensity to Save)
We also know that:
APC = C/Y
And,
MPS + MPC = 1
MPC = 1-MPS
Similarly,
APC + APS = 1
APC = 1 – APS
APS = 1 – APC
So, in the above question, saving is (-50) at 0 level of income, so Consumption would be +50 at 0 level of income. Here, APC is C/Y = 50/0 = infinity or undefined. Moreover, At 0 level of income MPS cannot be derived as MPS is percentage of additional income that is saved.
When Income increase from 0 level to 100, APC is 1. It means Consumption is equal to 100. So, saving is 0. Here, change in income (ΔY) is 100 while change in Saving (ΔS) is 50. So,
MPS = ΔS/ ΔY = 50/100 = 0.5
Now we can assume MPS constant at 0.5 and also investigate whether APC are same as given in the question.
When Income increases from 100 to 200, then increase in income (ΔY) is 100. If we take MPS as 0.5, then increase in Saving (ΔS) is 50. Here, total Saving is 0 + 50 = 50. Then consumption is = 200 – 50 = 150. So, APC = 150/200 = 3/4. The APC is accurate as per given question.
When income increases from 200 to 300, increase in income (ΔY) is 100. If we take MPS as 0.5, then increase in Saving is 50. Here total saving is 50 +50 = 100. Then, total Consumption is = 300 – 100 = 200. So, APC = 200/300 = 2/3. The APC is accurate as per given question.
Q.15. Reserve Bank of India undertakes the important function of managing the government’s banking transactions. Discuss the above stated function performed by the Reserve Bank of India. 4
Answer: RBI manages government banking transactions and as such it acts as banker to the government. RBI’s functions as a manager to government banking transaction are as below:
1. It maintains accounts of central and state government.
2. It accepts receipts and make payments on behalf of government.
3. It carries out exchange, remittance and other banking operations on behalf of government.
4. It also provides loans to government in case of need and emergency.
16.(a) (i) Distinguish between direct tax and indirect tax with the help of suitable examples.3
Direct Taxes | Indirect Taxes |
Impact and incidence of tax fall on the same person/entity of whom it is levied. | Impact and incidence of tax fall on different persons/entities. |
Burden of Taxes cannot be shifted to another person or entity | Burden of taxes can be shifted to another person or entity |
Example- Income tax is Direct Tax. Its final burden is born by the person on whom it is levied.
Goods and Services Tax – It is levied on goods and services at every stage of production process from actual production till goods reach to final consumers. However, it can be shifted and whole burden is born by final consumer.
(ii) Explain the redistribution of income objective of the Government Budget. 3
Answer: Redistribution of Income is one the objectives of the Government Budget. Under this objective, government aims to bring about equality in distribution in income in the country. To achieve this objective, government uses instruments of taxes and public expenditure.
It may impose high taxes on rich in the country in order to reduce their disposable income.
On the other hand, it may increase public expenditure for the welfare of the poor. It can also provide cheap or free goods and services to the poor to make them accessible for them. For example – PDS, govt. schools and hospitals.
In this way, government budget acts as a vehicle of bringing equality of income from its objective of redistribution of income.
OR
(b) (i) Suppose the following data is presented for an imaginary economy: Calculate Revenue Deficit and Fiscal Deficit based on this data. 4
S.No. | Items | Amount (in ₹ Crore) |
(i) | Tax Receipts | 1,200 |
(ii) | Revenue Expenditure | 3,700 |
(iii) | Non-Tax Receipts | 2,000 |
(iv) | Recovery of Loans | 145 |
(v) | Capital Expenditure | 500 |
(vi) | Disinvestment | 120 |
(vii) | Interest Payments | 1,070 |
Answer:
Revenue Deficit = Revenue Expenditure – Revenue Receipts
= (ii) – (i + iii)
= 3700 – (1200 + 2000)
= 3700 – 3200 = 500
Fiscal Deficit = Total Expenditure (Revenue Expenditure + Capital Expenditure) – Total Receipts (Revenue Receipts + Capital Receipts other than borrowings)
= (ii + v) – (i + iii + iv +vi)
= (3700 + 500) – (1200 + 2000 + 145 + 120)
= 4200 – 3365
= 735
(ii) Differentiate between public provision and public production. 2
Answer:
Public Provision – It means providing goods and services to public, financed through government budget. These goods and services can be obtained without any direct payment by the users. Example – Mid-day Meal.
Pubic Production – It means direct production of goods and services by the government. Example – Power production and supply by National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC), a Public Sector Company.
Q.17. Read the following text carefully:
Decisions taken by factors of production in the production process often may affect the stakeholders indirectly. Such impacts at times are huge but are not accounted for, while estimating national income. Economists call them as externalities and they can be positive or negative.
In this regard, many economists suggest carbon pricing as an important tool to ensure ecological balance.
Carbon pricing tries to control greenhouse gas emissions by either placing a fee on emitting or offering subsidies on lesser emission. Through instruments like carbon tax, green cess, eco tax, etc. economists suggest moving towards greener technology eliminating such negative externalities.
On the basis of the given text and common understanding, answer the following questions:
(i) Define externalities. 1
Answer: Externalities may be defined as benefits or harms received by persons without involving in the economic activities/production process.
(ii) Differentiate between positive and negative externalities. 2
Answer: Positive Externalities are those externalities which are received by persons/entities as benefits due to actions of other persons/entities. Example- Development of a private park also provides fresh air to others.
Negative Externalities are those externalities which are received by persons/entities as harms/penalties due to actions of other persons/entities. Example – Pollution by factories causes harms to general public.
(iii) Elaborate how and why carbon pricing should be promoted. 3
Answer: Carbon Pricing can be promoted by imposing fees or taxes on emission of harmful gases. However, less emission may be rewarded by providing subsidies.
Carbon Pricing should be promoted because it encourages use of less polluting technology or greener technology. This will help in mitigating negative externalities.
So, Carbon Pricing is very much needed to bring ecological balance.
Section B - Indian Economic Development
Q.18 During the British Rule, India’s foreign trade had various features except______________________.
(Choose the correct alternative to fill in the blank)
(A) Restrictive policies of commodity production, trade and tariff
(B) British monopoly over India’s exports and imports
(C) Free trade from India to the rest of the world
(D) Large export surplus
Answer: (C) Free trade from India to the rest of the world.
Explanation: During British Period, India could not trade freely with other countries. British government in India had placed several restrictions on production and trade. In case of foreign trade, they had monopoly over India’s exports and imports. Moreover, they had adopted discriminatory tariff policy towards finished Indian goods going out of country. They imposed heavy import duty in Britain on Indian Goods to make them costly in markets of Britain. Contrary to this, they imposed very less on nil import duty on British goods coming to India so that they could remain less costly in India.
In addition, it should be noted here that during British Period, India also witness large export surplus intermittently. However, this surplus was used by Britishers for their own benefit rather than the benefit of Indian People.
Q.19 China was able to control its rapid population growth rate owing to__________.
(A) Economic Reforms
(B) One- Child Policy
(C) Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution
(D) Special Economic Zones
Answer: (B) One- Child Policy.
Explanation: China remained highest populated country during the whole 20th Century. During 1970s, its population crossed 100 crores mark. To control growing population, China adopted One-Child Policy in late 1970s. In this policy, a couple could have only one child. This policy was strictly implemented and China was able to control its rapidly growing population. Its population growth rate fell from 2.63% per annum to 0.53% per annum in 2020.
This policy was abandoned in 2016 to start two child policy due to growing old age population. Further in 2021, China announced three child policy in which couple could have maximum three children.
Q.20 Modernisation is an important economic planning objective that focuses on ____________.
(Choose the correct alternative to fill in the blank)
(i) Adoption of innovative technology
(ii) Equal distribution of income and wealth
(iii) Bringing positive changes in the social outlook
Alternatives:
(A) Only (i)
(B) i and ii
(C) i and iii
(D) i, ii and iii
Answer: (C) i and iii
Explanation: Planning in India had four general objectives:
- Economic Growth
- Modernisation
- Equity
- Self-Reliance.
Under the objective of Modernisation, India was to adopt innovative technology for production of goods and services. Moreover, under this objective, bringing positive changes in the social outlook, especially society’s attitude towards socially weaker sections like women, was also focused.
Equal distribution of wealth and income is focus of the objective of Equity.
Q.21 The present day rapid industrial growth in China can traced back to the economic reforms introduced in 1978, where _________.
(Choose the correct alternative to fill in the blank)
(i) Initially reforms were initiated in agriculture, foreign trade and investment sectors.
(ii) the policy of dual pricing was adopted
(iii) the government revoked the policy of Special Economic Zone
Alternatives:
(A) Only (i)
(B) Only (ii)
(C) (i) and (ii)
(D) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer: (C) (i) and (ii)
Explanation: China has been one of the fastest growing large economy for many years. Its industrial sector has grown at a rapid rate which is evident from the fact that this sector contributes nearly 40 percent of its GDP. This rapid growth can be traced back to the reforms China Introduced in 1978. The main reforms were:
- Reforms were initiated in agriculture, foreign trade and investment sectors.
- Policy of dual pricing was adopted.
- Special Economic Zones were set up for attracting foreign Investment
Q.22 _____________farming is a system that is helpful in restoring, maintaining and enhancing the ecological balance.
(Choose the correct alternative to fill in the blank)
(A) Conventional
(B) Organic
(C) Chemical
(D) Multi-layered
Answer: (B) Organic
Explanation: After Green Revolution, farming changed considerably. We started using chemical pesticides and weedicides. However, due to continuous and overuse of chemicals, nutrient value in crops has decreased. These chemicals have also reached in our food-chain, causing various types of disease. To mitigate the harmful effect of agriculture with chemicals, Organic Farming has emerged an important alternative.
Organic Farming can be defined as a system of agriculture in which synthetic inputs like chemical pesticides are not used. Moreover, this type of farming relies upon crop rotation, crop residues, animal manures and other biological processes for growing crops.
Conventional and Chemical Farming system are related to use of chemical inputs in growing crops.
Multi-layered agriculture system involves growing multiple crops in a single field, either by planting one crop on top of another, or by growing plants of different heights in the same field at the same time.
Q.23 Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: India, Pakistan and China have similar physical endowments but totally different political systems.
Statement 2: Both India and Pakistan laid great emphasis on creating a large private sector.
(A) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(B) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(C) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
(D) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false
Answer: (A) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
Explanation: All the three countries have huge stock of natural resources. These have nearly similar physical endowments like huge plains, deserts, mountains etc. They also have vast lands for agriculture. However, they have different political systems. India has been a secular democracy since its independence in 1947. Pakistan is an Islamic state. It has been ruled by Army also for many years since 1947. On the other hand, China has been a communist state since 1949 and only one party has ruled it since then.
On the economic front, both India and Pakistan adopted Mixed Economics System which allows existence of both Public and Private Sector. However, they both laid emphasis on creation of a strong public sector, not the strong private sector. Only after economic reforms (1988 in Pakistan and 1991 in India), private sector could grow sufficiently.
Q.24 Identify the sources of Human Capital Formation and choose the correct alternative to fill in the blanks.
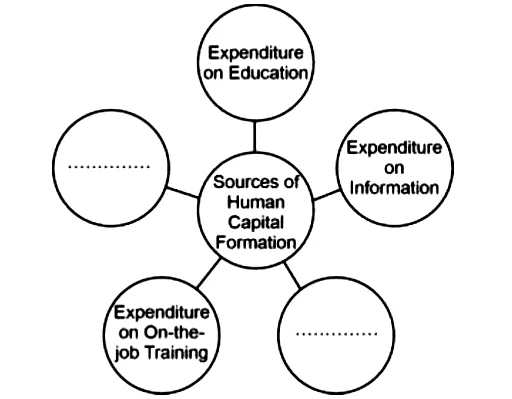
Credit: CBSE
Alternatives:
(A) Expenditure on Health and Expenditure on Schools
(B) Expenditure on Technology and Expenditure on Knowledge
(C) Expenditure on Migration and Expenditure on Knowledge
(D) Expenditure on Health and Expenditure on Migration
Answer: (D) Expenditure on Health and Expenditure on Migration
Explanation:
Human Capital Formation – It is a process of enhancing stock of ‘skill & expertise’ of a population in a country. The stock of skill and expertise is called the Human Capital.
There are five main sources of Human Capital Formation:
- Education: Making expenditure for getting basic & professional education from institutes like school & colleges.
- Expenditure on Health: Making expenditure on remaining healthy & disease free. For this, expenditure on hospitals is a major component.
- Expenditure on On-the-job training: It includes providing profession specific training to employees for further sharpening their skills.
- Expenditure on Information: Making expenditure and efforts to access information about job market and educational institutions so that potential of human being can actually be realized/achieved.
- Migration: People migrate from one place to another place to find better job opportunities so that their skills are better utilized at new place.
- Study Programs for Adults: School and Colleges, apart from formal education, also provide opportunities to students to participate in special study programs, often conducted by NGOs and Governments.
In the above question, three sources of Human Capital Formation are visible and remaining two have to be answered from the given options.
The first option has expenditure on school in it which is part of expenditure of education. The expenditure on Education is already visible in the picture. So this option is incorrect
The second and third options have expenditure on knowledge which is part of expenditure on education and expenditure on information. These are already visible in the picture. So, this option in incorrect.
The fourth option has expenditure on Health and Migration, two main sources of Human Capital Formation. These are not visible in the picture. So, this is the appropriate answer of the question.
Q.25 From the type of workers given in Column 1, identify the correct nature of the work in Column II:
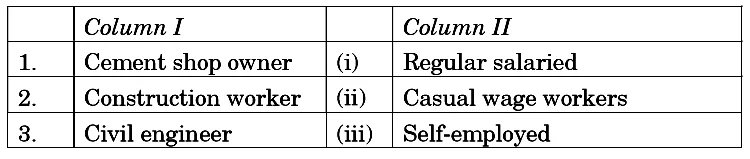
Credit: CBSE
Alternatives:
(A) 1-(i)’; 2- (ii); 3- (iii)
(B) 1-(ii); 2-(i); 3-(iii)
(C) 1-(iii); 2-(ii); 3-(i)
(D) 1-(iii); 2-(i); 3-(ii)
Answer: (C) 1-(iii); 2-(ii); 3-(i)
Explanation:
Self Employed Worker: A person who is engaged in his own work. He runs his business, mostly small businesses/works. They are not hired workers or work on salary. Example – Farmers, Shop owners etc.
Salaried Workers: These are hired workers who get regular salary from their employer. Example – Teachers, Clerks, Police Personnel, Engineers in a company etc.
Casual Wage Workers: These are also hired workers. Nature of their work is not regular. They mostly work on daily wage basis. Example – Agriculture workers, construction workers etc.
Q.26 After the implementation of economic reforms, Pakistan experienced slowdown of growth due to various reasons including_______________.
(Choose the correct alternative to fill in the blank)
(i) Volatile performance of the agriculture sector
(ii) Over-dependence on remittances from abroad
(iii) Political instability
Alternatives:
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(D) (i) and (iii)
Answer: (C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: Pakistan introduced economic reforms in 1988. However, these reforms could not result in better economic growth as expected. The main reasons for this were:
Political Instability: Pakistan has been a political instable country since its birth in 1947. It has been ruled by Army many times. Even after economics reforms, it was ruled by Army during 1999-2008. Army plays an important role even when there is a parliamentary government. It creates instability in political field which hampers implementations of economic decisions.
Volatile Performance of Agriculture Sector: As per scholars, agriculture growth was not sustained and also not based on institutionalized process of technical changes. It was based on good harvest. Whenever there was good harvest, economy of Pakistan would perform better. Economic growth would remain low due to poor performance of agriculture sector.
Over dependence on remittances from abroad: Supply of Foreign Currency in Pakistan was mainly due to remittances sent by its citizen from other countries, especially from Middle East countries like UAE, Saudi Arabia, Iraq etc. Instability in this regions since 1990 has impacted flow of foreign currency into Pakistan. Moreover, Pakistan has also been over-dependent upon foreign loans. These factors have badly affected its economy.
Q.27 Read the following statements: Assertion (A) ad Reason (R). Choose the correct alternative from those given below:
Assertion (A): In the recent past, Indian Economy has been facing the problem of jobless growth.
Reason (R): Jobless growth refers to a situation where an economy is able to produce more goods and services without generating employment.
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
Answer: B – Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation: Jobless growth refers to a situation where an economy is able to produce more goods and services without generating sufficient employment. In this situation economic growth surpasses the employment growth and there is widespread unemployment in the economy despite economy growing at healthy rate. Jobless growth mainly happens when technology replaces the human workers to a greater extent.
India is facing this situation for many years especially after 1991 reforms.
In the above question, both statements are true. But, we cannot say that (R) is the reason of (A) as the statement given in (R) is simply the definition of Jobless Growth and is not specifically related to the Indian Economy situation as mentioned in (A).
28.(a) Self-Help Groups provide stimulus to socio-economic development in rural areas. Justify the given statement with valid explanation. 3
Answer: It is true that self-help groups (SHGs) provide stimulus to socio-economic development in rural area. We can justify this statement due to following reasons:
1. SHGs fill the gap in rural formal credit system which is inadequate and not fully integrated in rural society.
2. SHGs provides small loans to its members on low interest rates, making them economically empowered.
3. Most of the members are women who can use loans from SHGs for small business opportunities and employment generation. So, SHGs promotes women empowerment.
4. Most members are from poor background. They may engage in fruitful social and economic decision making as member of SHGs.
Hence, SHGs can act as socio-economic development stimulus in rural areas.
OR
(b) Government of India has taken various measures to align the agricultural marketing system with the growing production activities in the rural areas. Do you agree with the given statement? Give any two valid reasons in support of your answer. 3
Answer: Yes, I agree with the given statement. The Government has taken following measures to align the agricultural marketing system with the growing production activities in the rural areas:
- It has opened many new regularized markets or Mandis to accommodate the growing production. Moreover, it has also made various market regulations for enhancing transparent market conditions.
- It has developed many infrastructural facilities like roads, cold storage, ware-houses etc.
Q.29. Interpret the given picture and explain any one strategy to control it from becoming an ecological disaster. 3
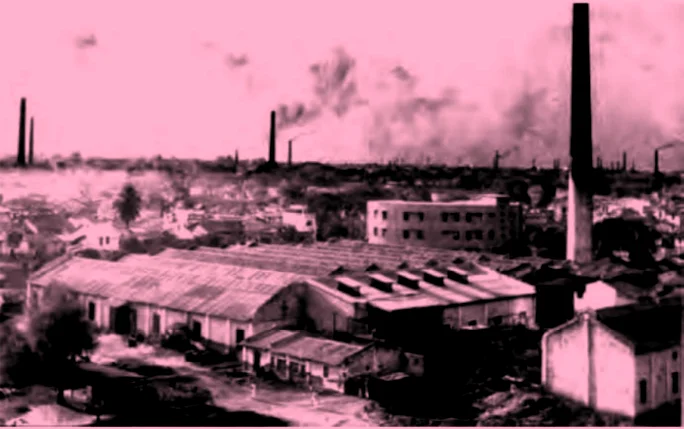

Credit: CBSE
Answer: The picture is related to air pollution caused by industrial activities. Factories release harmful gases and particulate matter into the atmosphere leading to environmental degradation. This could lead to harmful health effect and global warming.
In order to control air pollution, industries need to use greener technology of production. They should use cleaner and non-conventional sources of energy like solar energy, wind energy etc. Moreover, measures of carbon taxes and subsidies can be adopted to control emission of harmful gases.
Q.30.(a) Discuss any two factors that lead to stagnating Indian agriculture sector during British rule. 4
Answer: Indian agricultural growth was very low during British Rule. It was suffering with many problems which led to its stagnation. Following are the two factors responsible for the stagnation:
1.Land Settlement Systems: British Government adopted new land settlement systems and introduced Zamindars as middle-men to extract rent from the farmers. The rent was high and these Zamindars did not pay any attention for improvement of condition of farmers. They exploited farmers to extract the high rents, even in times of disasters like flood and droughts.
2.Irrigation & Technology: During British period, there were low level of irrigation facilities, backward technology, negligible use of fertilizers. These factors contributed in dismal performance of agriculture sector.
OR
(b) Discuss any two liberalization measures pertaining to the tax reforms, introduced by the government, during the economic reform process of 1991. 4
Answer: After 1991, India has also introduced some tax reforms as liberalization measures. Two of such measures taken by the government are as below:
1.Rates of direct taxes like income tax and corporation tax have been reduced in order to enhance tax compliance.
2.Indirect tax structure has also been simplified. Many indirect taxes were merged to form Goods and Services Tax (GST) to increase revenue and reduce tax evasion.
Note: Students may write another measures which is “Government simplified many procedure, especially tax filling, in order to enhance tax compliance.”.
Q.31. “There exists a positive correlation between human capital formation and economic growth of a nation.” Justify the given statement with valid explanation. 4
Answer: It is true that there may exist a positive correlation between human capital formation and economic growth of a nation. This statement is justified on the basis of following arguments:
1. An educated and Healthy population can provide continuous supply of highly skilled labour and contribute more in economic growth than the illiterate and unhealthy population.
2. Human Capital Formation enhances productivity, efficiency and capabilities of the population, resulting in higher economic growth.
3. Better education provides opportunities to understand the changes in society and scientific advancement. This helps in inventions and innovations.
4. Educated and skilled people can easily adapt to new technologies and help in stimulating the economic growth.
So, we can say that human capital formation is very much necessary to achieve higher economic growth.
Q.32 On the basis of the data given below, discuss the shift in output and employment sector-wise, in India and China: 4
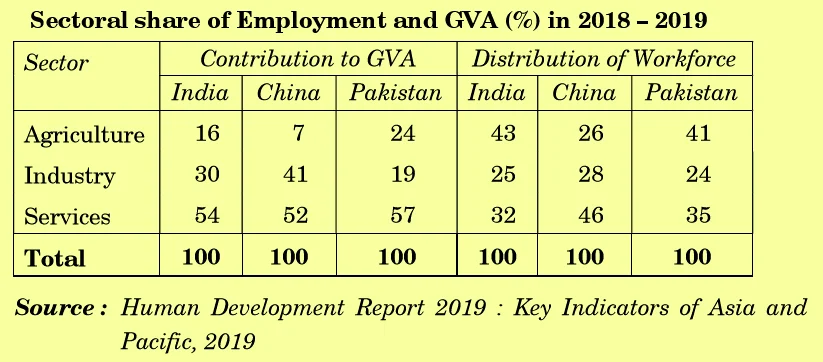
Credit: CBSE
Answer: Based on the given data in the table as per HDR-2019, we can make following observations regarding sectoral share of Employment and Gross Value Addition (GVA) of India and China:
1. India has most employment in agriculture which 43 percent of its total workforce. However, agricultural workforce contributes only 16 percent of total GVA in the country. On the other hand, contribution of agriculture is also very low in China to 7% only. However, China employs only 26 percent of its workforce in agriculture which very much less than India’s 43 percent. It may be due to less cultivable area in China than India.
2. In Industrial Sector, they both have similar workforce, 25 percent in India and 28 percent in China. However, China contribution of Industrial Sector in GVA is much more than that of India. With 28 percent of workforce, China contributes 41 percent of total GVA while India contributes much less 30 percent of total GVA with 25 percent workforce. It is probably due to higher labor productivity in this sector in China.
3. In the service Sector, GVA contribution is similar in both countries, with 54 percent in India and 52 percent in China. However, India employs much less workforce in this sector, with 32 percent in comparison of China’s 46 percent. In this, sector, India has higher productivity than China
Q.33.(a) (i) Amita is a regular worker in a private firm that employs twelve hired workers. Is she working in the formal/informal sector? Give valid reasons in support of your answer. 2
Answer: Amita is working in Formal Sector.
Formal Sector includes establishments which hires 10 or more workers. Amita is working in an establishment with 12 workers.
(ii) State any two sources of data on unemployment in India. 1
Answer: 1. Census of India
- Surveys conducted by National Sample Survey Office (NSSO)
(iii) Elaborate the need to promote Women’s education in India. 3
Answer: Due to following reasons, there is a need to promote women’s education in India:
- Women education with empower them socially which will bring gender equality in society.
- Women education make them financial independent to take their own financial decision.
- Women education can also make them more aware to bring down fertility rate in order to control population growth of India.
So, it is very much necessary to promote women education in India to bring positive socio-economic changes.
OR
(b) (i) The participation rate of people in economic activities in rural areas is more than that in urban areas. Justify the given statement. 3
Answer: It is true that percentage of rural population in labourforce is more than that of urban areas. This may be due to following reasons:
- There are more illiterate and poor people in rural areas than urban areas. So, rural people have to work at early age.
- Rural people have limited options for employment as compared to urban areas where there are various employment options. So, rural people can easily choose and indulge in employment activities.
- In contrast, People in urban area are more educated. With varied employment opportunities, they search for employment suitable for their skills and qualifications.
Hence, we can say that illiteracy, poverty and limited sources of employment causes higher participation rate in rural areas as compared to urban areas.
(ii) Define disguised unemployment. State its implications on output and employment in a country. 3
Answer: Disguised unemployment is a type of unemployment which refers to a situation where there are more workers indulged in a production process than needed. The extra workers do not contribute in increase of production. It means that their marginal productivity is zero.
Such unemployed persons do not contribute anything in output. Disguised unemployment does not contribute in employment generation also. Rather, it creates a situation of underemployment in which workers are not fully utilized to their potential.
Q.34. Read the following text carefully:
India’s industrial policy since independence has been shaped broadly in terms of the Industrial Policy Resolution of 1948. It emphasized on the sole responsibility of the government in the matter of promoting, assisting and regulating the development of industries in the national interest. It envisaged an active and dominant role of public sector.
The next Industrial Policy Resolution was placed before the Parliament by the Prime Minister on 30th April, 1956. It suggested that, there is a need for adoption of the socialist pattern of economy as the national objective, along with the need for planned and rapid development. It required that all industries of basic and strategic importance, or in public utility services, should be in the public sector.
Other industries which are essential and require investment on a massive scale (which only the State could provide) have also to be in the public sector. Thus, the State has to assume direct responsibility for the future development of industries.
This Resolution classifies industries into three categories:
The first category given in Schedule A, consists of industries the future development of which will be the exclusive responsibility of the State.
In the second category given in Schedule B, are industries which will be progressively State-owned. However, in them, private enterprise will also be expected to participate.
The third category comprises all the remaining industries, the further development of which will be left to the initiative and enterprise of the private sector.
On the basis of the given text and common understanding, answer the following questions:
(i) The Government of India, in the initial years of economic development, emphasized on a greater role of the public sector in the industrial development. Justify the statement, giving reasons in support of your answer. 3
Answer: It is true that after Independence Government of India laid great emphasis on development of public sector. It can be proved from the following actions of government:
1. Just after the independence, in Industrial Policy Resolution – 1948, the government envisaged dominant and active role of public sector in promoting Industrial Development in India.
2. Later in IPR-1956, it stated that all the industries of basic and strategic importance should be in the public sector.
3. The government felt that certain industries required massive investment which only the government could afford. So, some industries, especially heavy industries were development in public sector.
(ii) Outline and discuss the classification of industries into various categories as per Industrial Policy Resolution, 1956. 3
Answer: IPR-1956 categorised industries into three categories as below:
1.Schedule A Industries – This category consisted industries which were to be developed exclusively in Public Sector.
2.Schedule B Industries – This category consisted industries which were to be developed progressively in Public Sector. However, Private Sector could also participate.
3. Schedule C Industries – This category comprised all the remaining industries and they were left for private sector.
We hope that you liked our effort. You can appreciate our effort in comment section.
Link for other solved paper of Economics

CBSE Class 12 History Answer Key 2025 Paper Code 61/6/1 Free with explanation

CBSE Class 12 Biology Answer Key Paper Code 57/7/1 – with great accuracy

CBSE 2025 Economics Answer Keys Paper Code 58/5/1 – Free and accurate

CBSE class 12 Economics Answer Keys 2025 with explanation – Free and authentic


