Solved past year question papers are very helpful resource material for students to get maximum marks in final exams of CBSE. These papers help student to know the pattern of questions which are asked in CBSE exams. Economics, being one of the toughest subject at senior secondary level, requires a thorough preparation to get good marks in the final exams. In view of this, here we bring to you solved past year question paper of Economics for 12th class. This question paper (Code- 58/1/1) came in 2023 final exams in CBSE. Solution provided are in line with the official marking scheme of CBSE. Moreover, the explanation is provided in very easy language. You can also download this solved paper by clicking here.
SECTION A - INTRODUCTORY MACRO ECONOMICS
Q.1 Read the following statements carefully: (1 Mark)
Statement 1: Primary deposits are the cash deposits by general public with commercial banks.
Statement 2: Secondary deposits are those deposits which arise on account of credit provided by the commercial banks to the people.
In light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
a.Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false
b.Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true
c.Both Statements 1 and 2 are true
d.Both Statements 1 and 2 are false
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: Both statements are true as Primary Deposits are the deposits of people with the bank which they initially deposit while Secondary Deposits are deposits in loan accounts of the people which are created based on primary deposits.
Q.2 (A) The difference between National Income at market price and National Income at factor cost is . (Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank) (1Mark)
a.net indirect taxes
b.net factor income from abroad
c.consumption of fixed capital
d.market price
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (a) is correct.
Explanation: When you change concept of Factor Cost into Market Price, you need to add Net Indirect Taxes (Indirect Taxes-Subsidies) in Factor Cost. So, Factor Cost + NIT = Market Price
OR
Q.2 (B) Identify which of the following represents only the real flow: (1Mark)

Answer: Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: Real Flow involves flow of factor services from Household Sector to Producer Sector (Firm) and flow of Goods & Services produced in Producer Sector towards Household Sector. The Real Flow does not involve Monetary Transactions.
Q.3 The rate at which commercial banks borrow from the Reserve Bank of India to meet their long-term requirements is known as (Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank) (1 Mark)
a.Margin requirement
b.Bank rate
c.Repo rate
d.Reverse repo rate
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: Bank Rate is one of the quantitative tools of RBI to control credit flow through commercial banks in the economy. Commercial Banks take short-term and long term loans from RBI. Bank Rate is that rate at which Commercial Banks borrow from RBI for long term without any securities.
Q.4 Read the following statements carefully: (1 Mark)
Statement 1: Borrowings by a nation from the World Bank to finance Balance of Payment (BOP) deficit will be recorded in the capital account.
Statement 2: Autonomous transactions are independent of the condition of Balance of Payment (BOP) account.
In light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(c) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct:
Explanation: Borrowings create liability. Hence, they will be recorded under capital account. Autonomous transactions in BoP are not made to correct the balance of payment conditions (imbalance in BoP) and are independent of the conditions of BoP account. It is Accommodating Transactions which are made to correct imbalances in BoP account.
Q.5 Read the following news report carefully: (1 Mark)
“The central bank has imposed fine on Hisar Urban Cooperative Bank Ltd. and Andaman and Nicobar State Cooperative Bank Ltd. for violation of banking norms”
According to the given report, identify the function of the central bank.
(a) Issue of currency
(b) Banker to the public
(c) Banker to the Government
(d) Banker’s Bank
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (d) is correct.
Explanation: RBI as Banker’s Bank also plays a supervisory role over banks (formal sources of credit). In case of any violation of RBI’s rules, it may impose penalty.
Q.6 (A) If the value of investment multiplier = 4 and Dissavings = (-) 60, identify the correct Saving function from the following: (1 Mark)
(a) S = (-) 60 + 0·25 Y
(b) S = (-) 60 + 0·75 Y
(c) S = (-) 60 + 0·20 Y
(d) S = (-) 60 + 0·60 Y
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (a) is correct.
Explanation: Given the k (investment multiplier), we can calculate the value of MPS as below:
k= 1/MPS
4=1/MPS
MPS =1/4=0.25
Moreover, Saving Function is:
S= – C + MPS (Y) (here – C is dis-savings which is -60)
Then
S = (-60) + 0.25 (Y)
OR
Q.6 (B) For the given Consumption function, C = 205 + 0·9 Y, the value of investment multiplier would be (Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank) (1 Mark)
(a) 0·09
(b) 10·0
(c) 0·9
(d) 9·0
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: In the above consumption function, 0.9 is Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) and investment multiplier depends on MPC. Based on information given in above consumption function, we can calculate Investment Multiplier (k) as below:
k = 1/1-MPC
= 1 / 1-0.9
= 1 / 0.1
= 10
Q.7 Read the following statements: Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose the correct alternative given below: (1 Mark)
Assertion (A): Before reaching the Break-Even level of income, the value of Average Propensity to Consume (APC) is greater than one.
Reason (R): The Average Propensity to Consume (APC) is the ratio of the total consumption and total income.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: APC can be calculated as ratio of total consumption and total income, APC = C/Y. Value of APC before Break Even Point (BEP) is more than 1 because before this point total consumption is greater than total income. At BEP, C = Y and after this point C < Y. At BEP, APC is 1 and after BEP, it is less than 1.
Q.8 Suppose that, the Balance of Trade of a nation exhibits a deficit of ₹ 50,000 crore. The import of visible items are five times of the exports of visible items. The value of exports of visible items would be ₹………………crore. (1 Mark)
(Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank)
(a) 20,000
(b) 10,000
(c) 12,500
(d) 20,300
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: As per question, Balance of Trade (visible trade which is trade in goods only) of a nation exhibits a deficit of ₹50,000 crore. Deficit is Balance of Trade occurs when Import of visible items is higher than the Export of visible items.
So,
Import of visible items – Export of visible items = ₹ 50,000/-
However, import of visible items are five times of the exports of visible items.
Now suppose,
Export of visible items = a
Then,
Import of visible items = 5a
Now, as per information given in the question,
5a – a = 50,000
4a = 50,000
a = 50000/4
a = 12,500
OR
Q.8 (B) Gifts and remittances sent abroad are recorded on the………………….side of the……….account in Balance of Payment. (Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blanks) (1 Mark)
(a) credit, capital
(b) debit, capital
(c) credit, current
(d) debit, current
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (d) is correct.
Explanation: In Balance of Payment what goes out of the country is recorded on debit side and what comes in the country is recorded on credit side. So, Gift and remittances sent abroad will be recorded on debit side. Moreover, they do not reduce any liability. Hence, they will be recorded under current account in Balance of Payment Account.
Q.9 Identify which of the following equations is true. (1 Mark)
(a) MPC + MPS = 0
(b) MPC + MPS = 1
(c) MPC + MPS > 1
(d) MPC + MPS < 1
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (b) is true.
Explanation: If we take additional income as 1, then part of this additional income will either be consumed (MPC) or be saved (MPC). So, sum of the MPC and MPS will always be equal to 1.
Q.10 A situation in which an able-bodied person is not willing to work at the existing wage rate, is referred to as situation. (Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank) (1 Mark)
a.Full employment
b.Involuntary unemployment
c.Voluntary unemployment
d.Disguised unemployment
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct.
Explanation:
Full Employment: It is the level of employment at which all persons who want to work at existing wage rate get work. However, even in this situation, natural unemployment exists. In natural unemployment mainly two types of unemployment namely Structural Unemployment (occurs due to change in technology) and Frictional Unemployment (occurs when a person searches for a new job) are found in an economy.
Involuntary Unemployment: It is a situation in which not all who are willing to work at the existing wages get work. Some persons may remain jobless as they cannot get work at the existing wage rate.
Voluntary Unemployment: It is a situation of unemployment in which a person is not willing to work on existing wage rate and willing remains unemployed.
Disguised Unemployment: It is a situation in which more people are engage in a work than needed. The extra persons engaged in that work do not add to total production and hence their marginal productivity is 0. So, they can effectively be called disguised unemployed.
11 (A) Distinguish between ‘Value Addition’ and ‘Final Value of Output’.(3Marks)
Answer:
| Value Addition | Final Value of Output |
Definition | Value Addition means adding some value (in the form of increased price) to goods & services at every stage of production & distribution till they reach to their end user. | Final Value of output means total money value of goods and services produced during a given period of time. |
Formula | Value Addition = Value of Output – Value of Intermediate Consumption | Final Value of output = (Number of units produced) x (Price per unit) |
OR
Q.11 (B) Find the Value Added by Firm A, from the following information (3Marks)
S.No. | Particulars | Amount (in ₹ crore) |
(i) | Purchase of factor inputs by Firm A | 5 |
(ii) | Purchase of non-factor inputs by Firm A | 2 |
(iii) | Sales by Firm A to other firms in the domestic economy | 10 |
(iv) | Import of raw materials by firm A from rest of the world | 50 |
(v) | Excess of opening stock over closing stock | 3 |
Answer:
Value added = Value of output – Intermediate consumption.
Value added by firm A = (iii)- (v) – (ii + iv)
= 10 – 3 – (2 + 50) =
= 10 – 3-52 = -45
Explanation: Value of output consists of sales and change in stock. Change in stock can be calculated by deducted opening stock from closing stock. If closing stock is in excess over opening stock, then change in stock will be added to the sales. However, if opening stock is in excess over closing stock then change in stock will be subtracted from sales. In the above, example opening stock is in excess of closing stock by Rs. 3 crores. It means change in stock is 3 which will be deducted from the sales.
In case of intermediate consumption, expenditure done on intermediate goods is considered intermediate consumption. In the above question, the firm is end user of factor inputs like land, labour, capital etc. So they cannot be considered as intermediate goods. Hence, expenditure done on purchase of factor inputs will not be considered as intermediate consumption by the firm. Only expenditure on purchase of non-factor inputs and import of raw material will be considered as intermediate consumption.
Know More About National Income Accounting
Q.12 “There exists a positive relation between foreign exchange rate and supply of foreign exchange.” Do you agree with the given statement? Justify your answer with valid arguments. (3Marks)
Answer: Yes. Increase in foreign exchange rate leads to increase in supply of foreign exchange. Increase in foreign exchange rate means that one unit of foreign currency can buy more unit of domestic currency than before. This would result in increased purchasing power for the foreigner. Now, foreigners could purchase more quantity of a domestic good with one unit of foreign currency. In this way, demand for domestic goods will increase in abroad and this will lead to increased export. More export will bring more supply of foreign Exchange. Apart from increased export, increase of foreign exchange rate will stimulate increase in foreign investment in the country. This will result in increased supply of foreign exchange in the country.
Q.13 Describe the adjustment mechanism, if ex-ante savings are less than ex-ante investments. (4Marks) Answer: If ex-ante savings are less than ex-ante investments, following adjustment mechanism would follow to restore the equilibrium level in the economy:
- In this case, expenditure in economy is greater than what is required to buy the planned output.
- It becomes a situation of excess of AD over AS.
- This will lead to fall in inventories below the desired level.
- Thereafter, to fulfill the increased demand and to achieve the desired level of inventories, producers will increase output and employment in the economy.
- Increase in output and employment will result in increase in income which would in turn increase the level of ex-ante saving in the economy.
- The process of increasing output will continue until ex-ante saving increase to the level of ex-ante investment and equilibrium is restored.
Q.14 Read the following news published on September 26, 2022:
“The central bank has increased the benchmark lending rate by 140 basis points”
Identify the likely cause and consequences behind this action taken by the Reserve Bank of India. (4Marks)
Answer: Inflation may be the cause of increasing the benchmark lending rate by RBI.
Repo rate is the benchmark lending rate at which RBI lends to Commercial Banks. if RBI increases this rate, commercial banks are likely to hike interest rates for the general public. Due to increased cost of borrowing, the general public will make less demand for loans than before and it will lead to decrease in aggregate demand in the economy. Decrease in aggregate demand will help in controlling the inflation situation in the economy.
Q.15 (A) Explain the ‘Government’s Bank’ function of the central bank. (4Marks)
Answer: Central Bank function as government bank is one of the most important functions. As a government’s bank it may for form following functions:
- It manages government accounts for the purpose of receiving/making payments on its behalf.
- It performs function of a government agent by selling and buying securities on behalf of the government
- In the role of an advisor to the government, it helps in formulating policies to regulates the money market in the economy.
- It also provide loans to the government in time of need.
OR
Q.15 (B) Using a hypothetical numerical example, explain the effect of rise in Reserve Ratio on credit creation by the commercial banks. (4Marks)
Answer: Reserve ratio is the part of deposit in a bank which is mandated by the central bank to keep aside that cannot be used for lending purpose. However, the reserve ratio determines the volume of credit creation by the commercial bank. More the reservation ratio less the credit creation and less the Reserve ratio more the credit creation by the commercial bank. we can understand this by the following example:
Suppose the initial deposit is ₹1000. RR is 20%. Then volume of credit creation will be Rs. 5000. This can be calculated as below:
1000 x 1/20% = 1000 x 5 = Rs. 5000/-
Now Suppose RR increases to 25%, then volume of credit creation will be Rs. 4000/-. This can be calculated as below:
1000 x 1/25% = 1000 x 4 = Rs. 4000/-
In this way, we can see that there is inverse relationship between RR and volume of credit creation.
Q.16 (a) “National income is always greater than domestic income”. Do you agree with the given statement? Support your answer with a valid reason. 3M.
Answer: No, national income is not always greater than the domestic income. It all depends on the volume of net factor income from abroad (NFIA). NFIA is the difference between national income and domestic income. We can get national income by adding NFIA into domestic income. if NFIA is positive, then national income would be greater than the domestic income. However, if NFIA is negative then national income will be less than the domestic income.
Q.16 (b) “In the estimation of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) using expenditure method, focus lies only on expenditure by the residents of the country.” Do you agree with the given statement? Give valid reasons for your answer. (3Marks)
Answer: No, I do not agree with the given statement. Calculation of GDP through expenditure Includes all the expenditure on final goods and services by all the people within domestic Territory of a country irrespective of their residential status. As such, expenditure done by residents and non-residents within domestic territory will be included in calculation of GDP using expenditure method.
17 (a) (i) From the information given in the diagram, categorize the items into revenue receipts and capital receipts, stating valid reasons. (4Marks)
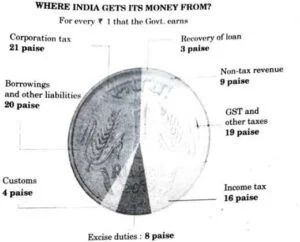
Answer:
Revenue receipts: Corporation tax, Customs, Income tax, Non-tax revenue,
GST and other taxes, Excise duties.
Reason: Revenue receipts neither decrease assets of the government nor they create liabilities for the government. Receipts like corporation tax, income tax etc. do not create any liability or decrease assets. They need not to be repaid back to the payer.
Capital receipts: Borrowing and other liabilities, Recovery of loan.
Reason: Capital receipts either decrease assets of the government or they create liabilities for the government. Receipts like borrowing create liability as they need to be repaid while recovery of loans decrease asset of the central government as in accounting sense loan create asset for provider of loans.
Q.17 (a) (ii) Distinguish between Revenue deficit and Fiscal deficit. (2Marks)
Answer: Revenue Deficit means excess of estimated revenue expenditure over estimated revenue receipts of the government during a fiscal year. However, Fiscal Deficit is excess of the total estimated expenditure over total estimated receipts (except borrowings requirement of the government) during a fiscal year. Revenue Deficit is part of Fiscal Deficit. Fiscal Deficit shows the total demand of the government for borrowings.
OR
Q.17 (b) (i) From the following data, calculate the primary deficit. (3Marks)
SNo. | Particulars | Amount (in ₹ crore) |
(i) | Revenue deficit | 40 |
(ii) | Non-debt creating capital receipts | 190 |
(iii) | Tax revenue | 125 |
(iv) | Capital expenditure | 220 |
(v) | Interest payments | 20 |
Answer: Primary Deficit: {(i) + (iv) – (ii)} – (v)
{40 + 220 – 190} – 20
₹ 50 Crore.
Explanation: Primary deficit is difference of Fiscal deficit and interest payments.
Fiscal deficit is excess of total expenditure(Revenue Expenditure + Capital Expenditure) over total receipts other than borrowings (Revenue Receipts + Capital Receipts other than borrowings). In the question, total expenditure will include Revenue Deficit (Revenue Expenditure>Revenue Receipts), Capital Expenditure while total receipts will include only non-debt creating capital receipts. Tax revenue will not be included separated as it is already included in Revenue Receipts.
Q.17(b)(ii) Elaborate ‘Economic stability’ function of the Government Budget. (3Marks)
Answer: Free Markets are likely to face business cycles which lead to phases of recession, depression, recovery and boom. These phases cause fluctuations in income, employment and prices in country. They also create situation of inflation and deflation in the country which leads to economic instability. Government uses the budget to correct the situation of inflation and deflation by imposing or removing taxes and increasing or decreasing government expenditure.
SECTION B - Indian Economic Development
Q.18 Read the following statements carefully: (1Mark)
Statement 1: Commercialization of agriculture under the British rule was responsible for frequent famines between 1875 and 1900.
Statement 2: During British rule, India began to export food grains.
In light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
a.Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false
b.Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true
c.Both Statements 1 and 2 are true
d.Both Statements 1 and 2 are false
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: Commercialization led to diverting of land use from food grain crops to commercial crops. Moreover, India also started to export food grain during British period. These factors created shortage of food-grain in the country which resulted in many famines in India during 1875-1900.
19 (A) Read the following statements carefully: (1Mark)
Statement 1: The purchase of food grains made by the Government on the Minimum Support Price (MSP) is maintained as buffer stock.
Statement 2: Minimum Support Price safeguards the farmers against any sharp fall in farm product prices.
In light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
a.Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false
b.Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true
c.Both Statements 1 and 2 are true
d.Both Statements 1 and 2 are false
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: Government purchases the food grains at MSP and store it as buffer stock. MSP has ensured the stability of selling price of food grains for farmer against fluctuations in market price.
OR
Q.19 (B) Identify the incorrect statement from the following: (1Mark)
a.Import substitution was the strategy used to save foreign
b.License policy ensured regional
c.Russian economic model was the base for the Indian economic
d.Small Scale Industries are one of the essential tools for employment
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: Russia (erstwhile USSR) was a socialist economy (In which only public sector exists) while India adopted Mixed Economic System (In which both private and public sector exist)
Q.20 Mini-hydel plants are good for the environment because: (1Mark)
(i). they generate electricity only for local
(ii). they do not change the land use
(iii). they rely on the perennial
Choose the correct alternative) Alternatives:
a.(i), (ii) and (iii)
b.(ii) and (iii)
c.(i) only
d.(i) and (ii)
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (a) is correct.
Explanation: Mini-Hydel plant are set up in hilly areas where water streams flow through-out the years. These plants target supply of electricity to local area only as electricity production is not in surplus. Moreover, these plants can be set up in small space and they do not require construction of water reservoir as in case of Big-hydel plants. So, they do not change land use pattern in the area.
Q.21 (A) The Great Leap Forward (GLF) campaign in China focused on .
(Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank) (1Mark)
a.Widespread industrialisation
b.New agricultural strategy
c.Privatisation
d.Economic reforms
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (a) is correct.
Explanation: Great Leap Forward was a policy adopted by China in 1958 to change Chinese Economy from agrarian economy to industrialised economy. People were encouraged to set small industries in the backyard of the house. Moreover, collective agriculture was encouraged through Commune System.
OR
Q.21 (B) India is not a member of which of the following regional / global economic groups? (1Mark)
a.European Union
b.BRICS
c.G20
d.SAARC
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (a) is correct.
Explanation: European Union is a regional economic group which consists of member countries from Europe only. As India is in Asia continent, it is not a member of EU. However, India is member of G-20, BRICS and SAARC.
Q.22 “Skill India” programme launched by the Government is not an attempt to increase in India. (Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank) (1Mark)
a.human capital formation
b.efficient utilisation of inputs
c.increase in GDP growth
d.inadequate spread of vocational education
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (d) is correct.
Explanation: Skill India programme was launched in July 2015. It aimed to train nearly 30 crore people by 2022 in different skills. Learning skills are part of vocational education and it helps in human capital formation. A skilled person can efficiently utilize the inputs in production process and help in increasing the GDP growth in the country.
Q.23 Identify the correct alternative with reference to the following statement: “Between 1966-76, Mao introduced this movement under which professionals and students were asked to work and learn from real life situations prevailing in the countryside of China.” (1Mark)
a.Commune System
b.Great Leap Forward
c.Open Door Policy
d.Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (d) is correct.
Explanation: After setbacks form the Great Leap Forward programme, Chairman of Chinese Communist Party, Mao Zedong introduced Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution in mid 1960s. Under this programme, students and professionals were sent to work and learn from the rural areas. Moreover, the programme also aimed at instilling revolutionary values in the young generations.
Q.24 Read the following statements carefully: (1Mark).
Statement 1: In both India and Pakistan, the service sector has been emerging as a major source of development.
Statement 2: Amongst the neighbours of India, China has the highest life expectancy rate.
In light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(c) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: Both India and Pakistan has an emerging service sector which contribute maximum share in the GDP of these countries. With respect to life expectancy at birth, China is ahead of both India and Pakistan. This may be due to the rapid economic development China has made since 1980.
Q.25 (A) Workers who are on the permanent pay-roll of their employer are called workers.
(Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank) (1Mark)
(a) self-employed
(b) casual
(c) regular
(d) hired
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: Worker hired by an employer can be regular worker or casual workers. Regular workers are those workers which are on permanent pay-roll of the employer and they enjoy higher facilities than casual/temporary workers.
Self-employed are those type of workers which are not hired by anyone and they do their own work/business.
OR
Q.25 (B) Jobless growth leads to unemployment because. (1Mark)
(Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank)
(a) Labour refuses to migrate
(b) Labour is very expensive
(c) Growth rate is low
(d) Growth is due to technological development
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (d) is correct.
Explanation: Technology progress may lead to replacement of workers in production process. However, it may increase output, leading to economic growth. However, this growth will be technology driven not the employment driven.
Q.26. Production of diverse varieties of crops rather than one specialized crop is called. (Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank) (1Mark)
(a) diversification of crops
(b) diversification of agricultural production
(c) diversification in sectors
(d) diversification of employment
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (a) is correct.
Explanation: On a piece of land, we may grow different types of crops. We may grow wheat, rice, vegetables on a single piece of land in different seasons. Growing different types of crops is called diversification of crops.
Q.27 Read the following statements carefully: (1Mark).
Statement 1: India announced its First Five Year Plan in 1951.
Statement 2: India, Pakistan and China adopted economic planning as the core development strategy.
In light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(c) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false.
CBSE-2023 Code 58-1-1
Answer: Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: Taking inspiration from socialist Russia, India adopted economic planning as a core development strategy. It formed Planning Commission in March 1950 and launched 1st Five-Year plan in 1951. Pakistan adopted similar economic policy as India and launched its 1st Five Year Plan in 1956.
China, being a communist country, naturally adopted planning as core development strategy and launched it 1st Five Year Plan in 1953.
Q.28 Interpret the given picture, on account of current environmental challenges: (3Marks)

Answer: The picture shows the deforestation which can be defined as large scale cutting of tress in forest. These tree are mainly cut down for development project and excessive demand of wood in various industries. The deforestation can lead to many environmental challenge as following:
- It may lead to loss of biodiversity as many species may die during the process.
- Forest is home of many species and deforestation can lead to loss of natural habitats for these species.
- Trees are a natural factor to mitigate soil erosion. Cutting of trees will result in rapid soil erosion.
- Trees are natural storehouse of carbon-dioxide which is responsible for global warming and climate change. So, deforestation may lead to increase in level of carbon-dioxide in the environment causing global warming and climate change.
Q.29. (a) Critically evaluate the role of rural banking system in the process of rural development in India. (3Marks)
Answer: Rural banking has been an important factor in stimulating rural development. It has positively affected rural farm and non-farm sector, increasing the employment and income. However, there are some shortcomings as below:
Less Coverage: rural banking has not sufficiently covered the population of rural India. Credit volume through banking system is still insufficient.
Less attention to poorer section of society: The banking system has failed to target the small & marginal farmer and people doing petty works. They have little asset to use as collateral to get loans from the banking system.
Recovery problem: Loans taken by people are not paid off timely. In this case, there is huge overdue loan and banks have not evolved an efficient mechanism to recover the loans.
OR
Q.29. (b) Dr. Khurana, a dentist, ran his clinic in an economically backward area. He was earning a comparatively low income. So, he decided to move to a city and spent a huge amount for the same.” Identify and explain the type of expenditure incurred by Dr. Khurana, which directly contributed to the process of human capital formation. (3Marks).
Answer: The expenditure done by the Dr. Khurana is ‘Expenditure on Migration’. The expenditure on migration is considered a source of human capital formation. People, especially technically qualified persons, migrate from one place to another place in hope of getting employment and higher income opportunities. At the migrated place, they use their skill and earn more what they were earning at their earlier place. It helps them in formation of human capital.
Q.30 Explain valid reasons for the slow growth and re-emergence of poverty in Pakistan. (4Marks)
Answer: The reasons for the slow growth and re-emergence of poverty in Pakistan are:
- Like India, a huge part of population of Pakistan is engaged in agriculture sector. However, their agriculture growth was not based on technical change but on good harvest. Pakistan faced a volatile performance in the agriculture sector. So, Pakistan could not generate enough agriculture surplus.
- Pakistan has been over-dependent on foreign aid and remittances. After 1990, Pakistan’s remittances went down. Moreover, Pakistan has faced difficulty in paying back its loan which deteriorated Pakistan’s credibility. So, Pakistan has been lacking funds for development.
Q.31 (a) Explain briefly the rationale behind the ‘License Raj’ under the Industrial Policy Resolution, 1956. (3Marks)
Answer: License Raj under the Industrial Policy Resolution-1956 had following objectives:
Regional Equality: The government wanted to use to policy of license for development of economically backward regions in the country. To enhance regional equality, the government made a provision that firms could get license more easily in case they set up production units in backward areas.
Control over private sector: The government wanted to control the spread of private sector which is based on motive of earning profit only not on welfare motive. No new industry was allowed unless a license was obtained from the Government.
Control over production: The government wanted to control the production of goods and services in the country. By introducing License, it aimed to allow production of only those goods and services which it thought were necessary for the development of the country at the time.
Q.31 (b) Define Multilateral trade. (1Mark)
Answer: Multilateral trade means trade between more than two nations.
Q.32 (a) State and elaborate whether the following statement is true or false, with valid arguments: (4Marks)
“Indian economy has showed satisfactory progress towards formalization of workforce in the recent past.”
Answer: The statement is false. During the recent a past, India has faced the problem of informalisation of workforce. Workers who were earlier working in formal sector have shifted to informal sector. The reason for the same could be adverse effect of globalization which has resulted in shutting down of many local factories. Moreover, there is a declined in the job opportunities in formal sector (both private and public sector). Further, private sector now a days has a tendency of employing workers on need basis or temporary basis. When there is no need of their work in particular time period, the workers are left unemployed and forced to work in informal sector.
OR
Q.32 (b) “In India, the self-employed constitute around 60% employees. The possible incidence of under employment is the highest among the self-employed.”
As an economist, suggest and elaborate any two measures that may be taken to ensure more productive employment for the self-employed. (4Marks)
Answer: Two measures to ensure more productive employment for the self-employed are:
Better education and Skill development: Education plays an important role in increasing the productive of human capital. Moreover, training a person in a particular skill with the help of advance technology can also further increase the productivity of a person manifold.
Financial Support: Productive activities are very much dependent on financial resources. Maximum self-employed persons lack financial resources. So, government should provide them loans at lower interest rates with easy paying terms. The credit can enable them to use advance technology and thus increasing their productivity.
Q.33 (a)(i)Why are less women found in regular salaried employment.(3Marks)
Answer: Women are found less in regular salaried employment due to following reasons:
(i) Lack of Education: Female education has not been given much importance as compared to men’s education. So, most of the women lack required education and professional qualification for regular salaried jobs.
(ii) Family constraints: Most of the Indian families are orthodox which do not want that their women remain outside of house for long hours. Regular jobs demand long working hours and this becomes an obstacle for women. Moreover, traditionally women have to do all the household work and bear the responsibility of upbringing of the children.
Q.33 (a) (ii) Distinguish between human capital and physical capital. (3Marks)
Answer:
Human capital:means the stock of knowledge, skill and ability in a person. It is intangible in nature and inseparable from its owner. It cannot be sold in the market, only its services can be sold in the market.
Physical capital: It is that capital which is tangible in nature. They could be assets like plants and machinery. It is separable from its owner and can be sold in the market.
OR
Q.33 (b) (i) State and discuss any one strategy involved in attaining sustainable development in India. (3Marks)
Answer: Mini-hydel Plants-In mountainous regions, streams can be found almost everywhere. A large percentage of such streams are perennial. Mini-hydel plants use the energy of such streams to move small turbines. The turbines generate electricity which can be used locally. Such power plants are environment-friendly as they do not change the land use pattern.
Q.33 (b) (ii) Discuss briefly the importance of micro credit programme in rural India. (3Marks)
Answer: Micro-credit programmes such as self-help group have emerged to fill the gap in the formal credit system. The formal sources of credit like bank have not been very much successful in catering to the needs of poorer section of society. The major cause for this is the requirement of collateral for taking loans. Since, most of the poor rural households do not have collateral, they remain outside the ambit of credit system. Micro credit system provides these rural household to take smaller loan for their small needs at low interest rate. Moreover, they do not need collateral for taking such loans. These programme have emerged a major force in eradicating absolute poverty in India. As most of the members and beneficiaries are women, these programmes have financial empowered rural women.
Q.34 Read the following text carefully:
According to NITI Aayog, India has a technological advantage to facilitate digital banks. There is a need for creating a regulatory framework for promoting this. NITI Aayog, in its report titled “Digital Banks: A Proposal for Licensing and Regulatory Regime for India”, offers a template and roadmap for a digital bank licensing and regulatory regime for a country. India’s public digital infrastructure, especially Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has successfully faced this. With Aadhar, India is at the cusp of operationalizing its own open banking framework. This demonstrates that India has the technology stock to fully facilitate digital banks. Digital banking allows a user to set up automatic payments for regular utility bills. Digital banking enables fund transfers to reduce the risk of counterfeit currency. By promoting a cashless society, digital banking restricts the circulation of black money.
On the basis of the given text and common understanding, answer the following questions:
(a) Which institution has been replaced by NITI Aayog in India? Who is the ex-officio Chairman of NITI Aayog? (2Marks).
Answer: NITI Aayog has replaced Planning Commission.
Prime minister is the ex-officio Chairman of NITI Aayog.
(b) State and discuss any two main advantages of digital banking. (4Marks)
Answer: Two main advantages of digital banking are:
(i) Cashless Society: Digital banking help in achieving the goal of a cashless society. It restricts the circulation of black money.
(ii) Convenience: It enable users to set up automatic payments for regular utility bills. Thus, it provides a convenient method for customers to settle payments.

CBSE Class 12 History Answer Key 2025 Paper Code 61/6/1 Free with explanation

CBSE Class 12 Biology Answer Key Paper Code 57/7/1 – with great accuracy

CBSE 2025 Economics Answer Keys Paper Code 58/5/1 – Free and accurate

CBSE class 12 Economics Answer Keys 2025 with explanation – Free and authentic



